Shunted vs. non-shunted sockets: How to tell what you need
As we often mention on this blog, lighting is complex.
Sockets often intimidate a lot of our customers because there are multiple options. Do you need shunted or non-shunted sockets? And what's the difference?
But we're here to make supply – and sockets – easier. Understanding the difference between shunted and non-shunted sockets doesn't have to be rocket science, but it is important. Using the wrong type can cause an electrical short, resulting in a fire hazard and melting the sockets, tubes, or both. It can also void the UL listing on your lamp or shorten the life of the lamp.
And while we're at it, we should explain that sockets are also called tombstones or lamp holders. They all serve the same purpose: to hold the lamp in place and provide electricity. Think of a socket as the electrical receptacle for the light bulb.
In this post, we will share some guidelines for telling the difference between shunted and non-shunted sockets and where to use them.
Do you know what kind of sockets you need?
What's the difference between shunted and non-shunted sockets?
The difference between shunted and non-shunted joints is relatively simple, once you understand how each type works.
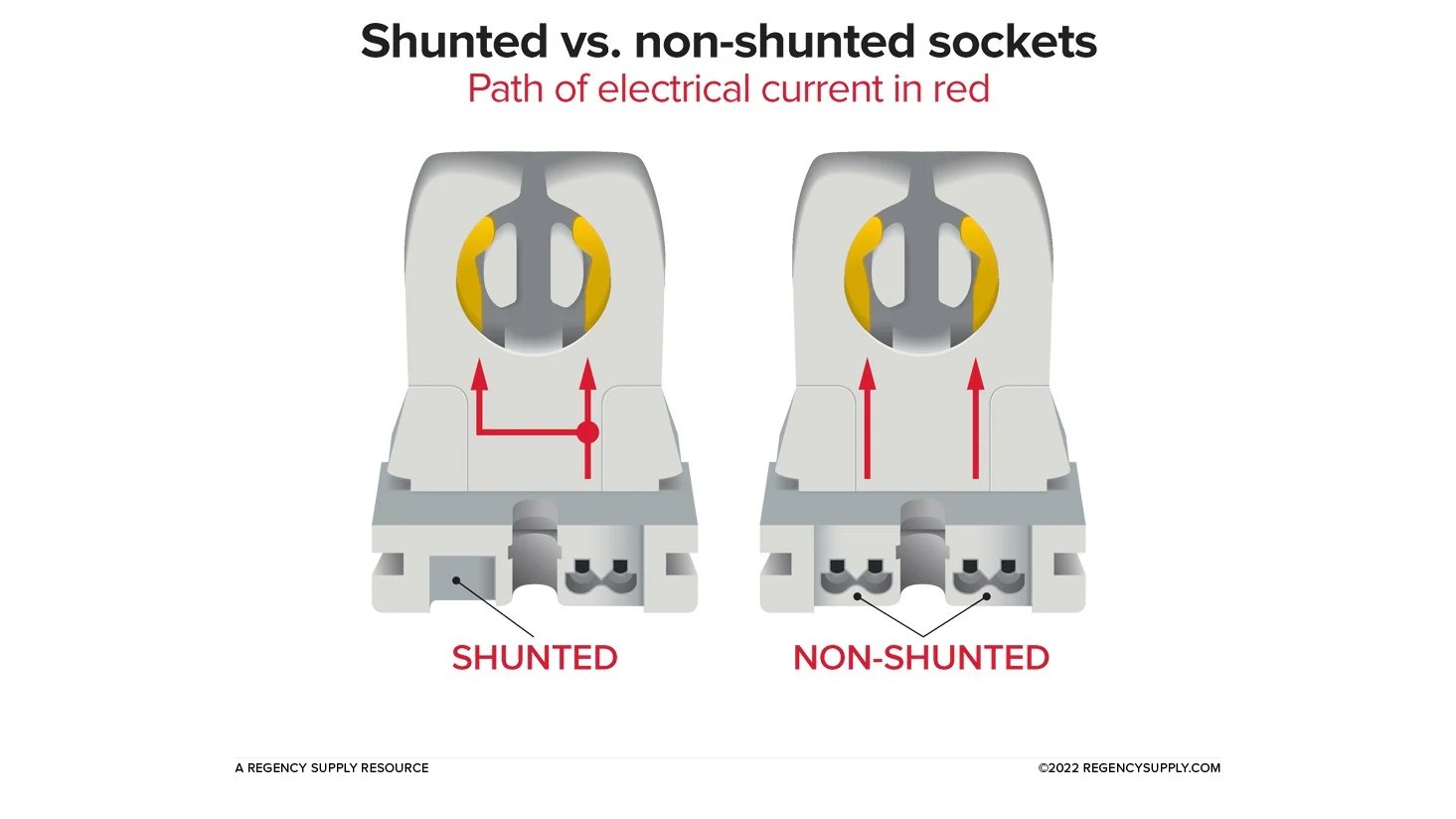
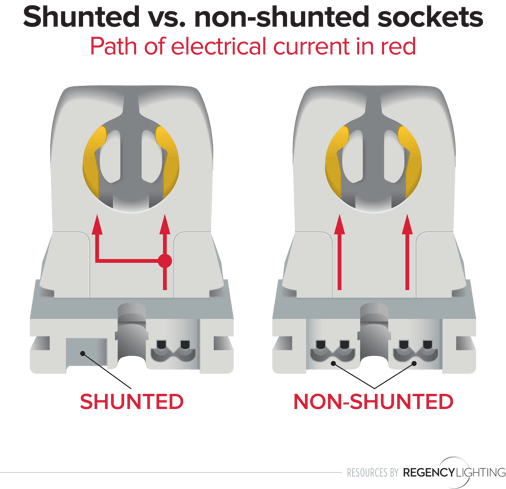
When you hear the word "shunted," think "joined" or "connected". Shunted sockets feature internally connected electrical contacts. This provides a single track for the electrical current to travel from the ballast, through the tombstone, or socket, and to the lamp's pins.
Non-shunted sockets have separate contacts – or points of entry for the wires – creating two tracks for the electrical current to travel. Non-shunted sockets have contacts that are not joined or connected.
The diagram below visually demonstrates the difference you'll most often see between the two types of sockets.
Because there are exceptions to this visual difference, the safest way to figure out what kind of sockets you have is to use a voltage meter. Most voltage meters will either light up or ring or beep if the electrical contacts are connected, or shunted.
Pro tip
Shunted sockets receive voltage through a single set of wires and spread it to two contacts. Non-shunted sockets send voltage to each of the contacts, through two wiring tracks.
When to use shunted sockets and when to use non-shunted sockets
Now that you understand how shunted and non-shunted tombstones work and how they are different, let's dive into when to use which type. The secret here: it really depends on the ballast for fluorescent tubes and the lamp type for LED tubes.
Click here to watch our video series on shunted vs. non-shunted sockets.
Please note: the table below is meant to reflect broad-sweeping general recommendations for socket pairings, but there are exceptions. For example, there are T8 plug-and-play LEDs made to work with rapid-start ballasts and programmed-start ballasts, requiring non-shunted sockets. Always double check with your lighting specialist or the lamp manufacturer to know what sockets you need.
| Lamp/Ballast
Bi-pin lamp type |
Socket Type
Shunted or non-shunted? |
| T12 | Non-shunted |
| T8 with rapid-start, programmed-start, or dimming ballast | Non-shunted |
| T8 with instant-start ballast | Shunted *Non-shunted (with external wire shunt) |
| T5 with rapid-start, programmed-start, or dimming ballast | Non-shunted |
| T5 with instant-start ballast | Shunted |
| LED T8 plug-and-play | Shunted |
| Single-ended LED T8 direct wire (or ballast-bypass) |
Non-shunted |
| Double-ended LED T8 direct wire (or ballast-bypass) |
Most compatible with Shunted and Non-shunted |
| LED T8 remote driver | Non-shunted |
| LED T5 plug-and-play | Shunted |
*There is the option to externally shunt a non-shunted socket with wires if you're looking to adapt a non-shunted socket for an instant-start ballast. But, frankly, you may be better off buying new shunted sockets to avoid a lot of wiring work, especially if you have a large number of sockets to manually shunt.
There is quite a bit of risk involved if you do not buy the right sockets, so if you have any questions, don't hesitate to speak with your lighting specialist.
We also sell more than light bulbs and sockets. If you're ready to purchase, apply for an account to receive business pricing.

This article was originally published in 2016. It has been updated with the latest lighting technology.